s,p,d,f block elements periodic table
Introduction:
The periodic table, a fundamental cornerstone of chemistry, is a powerful tool that helps us understand the properties and behavior of various elements. It classifies elements into distinct blocks, each with unique characteristics. In this blog post, we will embark on an enlightening journey through the S, P, D, and F block elements, uncovering their fascinating features, and exploring their crucial roles in the world of chemistry.
1. The Periodic Table: A Brief Overview
Before we delve into the specifics of the S, P, D, and F block elements, let's take a moment to understand the organization of the periodic table. Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, is credited with its creation in the late 19th century. The periodic table arranges elements in order of their atomic number, which reflects the number of protons in their nucleus. Elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together into columns known as groups, while elements with the same number of electron shells reside in the same rows called periods.
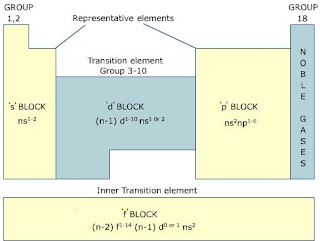
2. The S Block Elements: Group 1 and 2
The S block elements encompass the first two groups of the periodic table - Group 1 (alkali metals) and Group 2 (alkaline earth metals). These elements are characterized by their tendency to lose electrons and form positively charged ions. Alkali metals are incredibly reactive, and they react vigorously with water, while alkaline earth metals are less reactive but still play essential roles in various chemical reactions and biological processes.
3. The P Block Elements: Group 13 to 18
Moving along the periodic table, we encounter the P block elements, which include Group 13 to 18. These elements exhibit diverse chemical behaviors, with some being metals, nonmetals, or metalloids. Group 17, known as the halogens, is especially noteworthy for its strong reactivity and ability to form salts. On the other end, Group 18 consists of noble gases that are chemically inert due to their stable electron configurations.
4. The D Block Elements: The Transition Metals
Next, we encounter the D block elements, which occupy the space between Groups 3 and 12. These elements are commonly referred to as transition metals due to their unique electron configurations. Transition metals possess partially filled d orbitals, making them excellent catalysts and facilitating their involvement in numerous redox reactions. Their versatility finds applications in industries like medicine, electronics, and metallurgy.
5. The F Block Elements: The Lanthanides and Actinides
Finally, the F block elements, situated at the bottom of the periodic table, encompass the Lanthanides and Actinides series. These elements have partially filled f orbitals, which contribute to their magnetic properties and distinctive electronic configurations. The Lanthanides are often used in various technological applications, including lighting, magnets, and lasers. The Actinides, on the other hand, are radioactive elements, some of which have significant importance in nuclear energy and medicine.
6. Unique Properties and Applications
Throughout our exploration of the S, P, D, and F block elements, we will discover their diverse properties and the fascinating applications they hold in various fields. From the alkali metals' role in powering batteries to the noble gases' use in lighting, each element plays a vital part in our daily lives and technological advancements.
7. Unraveling Electron Configurations
A critical aspect of understanding the behavior of elements lies in comprehending their electron configurations. We will delve into the principles behind the Aufbau principle, Hund's rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle. By grasping these fundamental concepts, we can decipher the unique electron arrangements of different elements.
8. The Periodic Trends of S, P, D, and F Block Elements
As we progress, we will unveil the periodic trends displayed by these elements. These trends encompass atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and metallic character, providing us with valuable insights into their reactivity and chemical behavior.
9. Exploring Chemical Bonding and Reactivity
The distinctive electron configurations of the S, P, D, and F block elements significantly impact their bonding abilities. We will explore the types of chemical bonds they form, such as ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Moreover, we will analyze how these elements participate in chemical reactions, influencing their reactivity and role in various chemical processes.
Conclusion: The Marvels of the Periodic Table
In conclusion, the S, P, D, and F block elements form the backbone of the periodic table, revealing the vast diversity of chemical elements and their properties. Through our journey, we have uncovered the unique characteristics and applications of each element group. The periodic table stands as a testament to the remarkable achievements of human understanding of the natural world, and the S, P, D, and F block elements exemplify the wonders that chemistry has to offer.
As we continue to explore and unravel the secrets of these elements, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and interconnected nature of the universe. Embracing the beauty of the periodic table allows us to unlock the potential for new discoveries, innovations, and advancements that can shape our world for generations to come.



No comments:
Post a Comment
if you have any assignment problem please contact us